IEEE MLSP Data Competition
The Sampling-Assisted Pathloss Radio Map Prediction Data Competition, IEEE MLSP 2025
Motivation
Accurate prediction of pathloss (PL) maps in indoor environments is fundamental to applications including fingerprint-based localization, user-cell site association and path planning.
Traditional methods such as ray-tracing are usually computationally expensive and time-consuming. There exist gap between simulated and realistic data and lack generalization ability to different, unseen environments.
Contributions
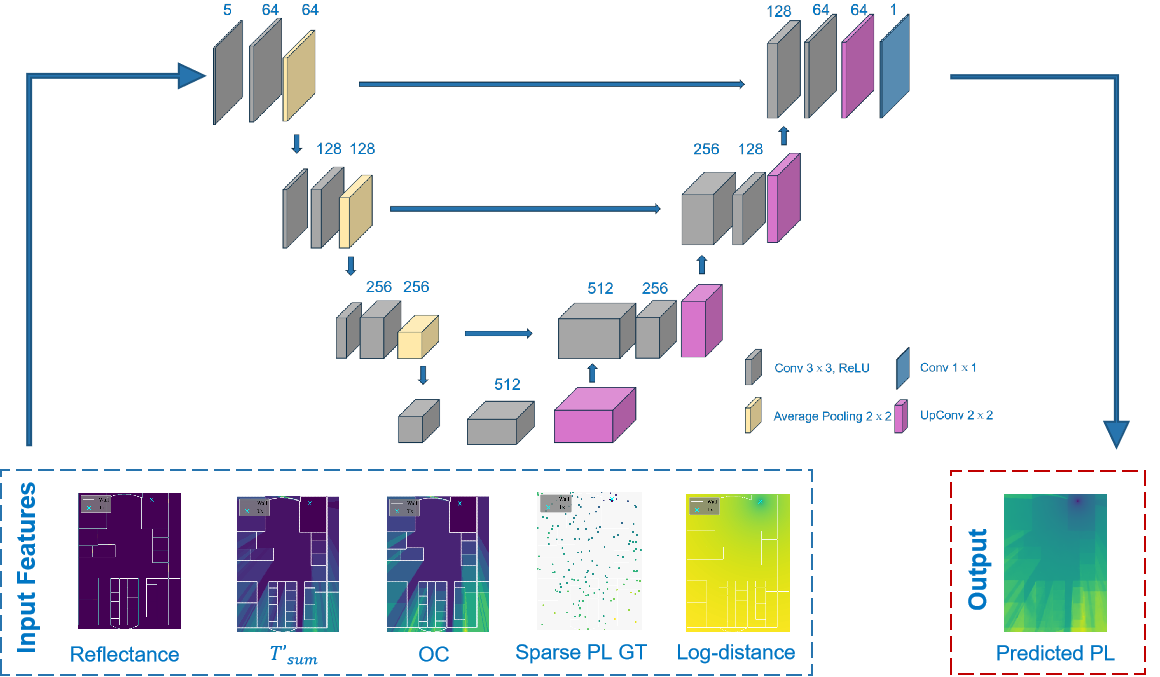
Thus, we developed a runtime-efficient U-Net model for 2D indoor pathloss predition under sparse sampling conditions, integrating environment-aware geometric features to enhance cross-environment generalization. Our method is data-driven, utilizing lighter and more efficient network and real-world measurements, and adaptive to different environments.
Our main contributions are twofold:
- Integrated environment-aware geometric features such as accumulated transmittance, obstruction counts to enhance cross-environment robustness
- Designed a lightweight U-Net model to maximize feature learning and generalization, while minimize runtime
Results
We achieved average total runtime of 14.36 ms and received 2nd place in this data competition.
The ablation studies shows 2 important insights:
- Setting 6 which integrates the full set of engineered inputs achieves the lowest validation RMSE.
- Even sparse PL inputs provide essential guidance for accurate map reconstruction.

For more system infomation please refer to our paper.